Network Softwarization in 5G
Network and computing infrastructures leverage the Network Softwarization for the design and operation of the services with greater agility and cost-effectiveness. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) are the critical technologies for realizing the network softwarization. The main idea of NFV is to decouple the software from the dedicated network function hardware equipment and install it onto virtual machines deployed on a virtualized commodity servers. SDN helps to separate the control plane from the data plane and connects different Virtual Network Functions (VNF) distributed over different datacenters. Together SDN, NFV, and Cloud are driving a transformation of networks.
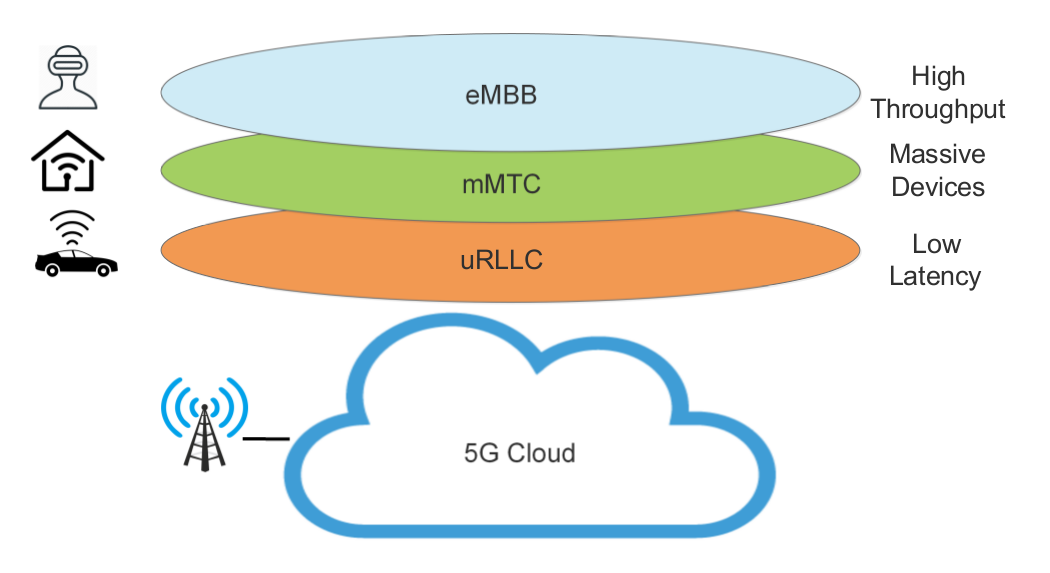
Based on the requirements of diversified use cases of 5G, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) classified the use cases of 5G into three broad families, namely enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), and ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (uRLLC). eMBB aims to focus on services that require high bandwidth and sustained high capacity network connections, such as High Definition videos, Augmented Reality, etc. The uRLLC services are required for applications like Factory Automation, Intelligent Transportation Systems, etc., which have latency constraints and need high reliability and availability. mMTC focuses on services that include high demands for connection density, such as smart agriculture, smart city, etc. Network Slicing is the key to 5G network architecture evolution to support diversified 5G use cases. Network Slicing allows the mobile network operator (MNO) to split a single shared physical network into multiple logical or virtual networks. Network Softwarization plays a significant role in enabling the Network Slicing.
Service Function Chaining (SFC) is an ordered set of Network Functions (NFs) which guides traffic through them to provide different end-to-end services. Network slicing runs on the principles of SFC, where multiple logical networks are run on top of a single shared physical network.
| Problem | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource Provisioning for the Network Slices in 5G Core Network |
Given variety of services running over the core network, the resource need for the services differ. The resources at the core network are bandwidth, processing, latency etc. Appropriate provisioning of these resources needs to be done based on type of network slice for efficient resource utilization and also guaranteeing the Service Level Agreements of the users. |
| Lifecyle management of VNFs in the SFCs | Typically, VNFs are run on top of Virtual Machines (VMs) which run on physical nodes in data centers. For each class of service, based on its policy, the traffic has to pass through a set of VNFs in sequence termed as Service Function Chains (SFCs). Selection of available VNFs to steer the SFC requests with guaranteed end-to-end latency is still an open problem and needs to be addresses. |
| Auto Scaling of VNFs | An Auto Scaling Entity (ASE) monitors the load on a VNF and scales up services depending on its usage. The ASE checks the load at each time interval called monitoring period and the VNF needs to wait for cooldown period to ensure that scaling action takes place. Existing algorithms, used by the operators to scale the VNFs, use a static cooldown period. Therefore, efficient algorithms are needed for dynamic adaptation of cooldown period for scaling of the VNF. |
| Efficient management of virtual radio resources between slices | On RAN part, one of the main challenge is how effectively distributing the radio resources to different slices dynamically. In literature, most of the approaches are allocating virtual radio resources to slices either statically or dynamically. In static slicing, it can achieve resource guarantees but drawback is resource underutilization. Using dynamic approach, resources can be utilized efficiently by assigning to overloaded slice from underloaded slice. But it is unclear how often dynamic resource allocation should be performed to obtain significant performance gains over static resource allocation. |
Research Scholars : Venkatarami Reddy (Ph.D),Tulja Vamshi Kiran Buyakar (M.Tech), Gaurav Garg (M.Tech), Mohit Kumar Singh (M.Tech), Harsh Agarwal (B.Tech)
[C1] Tulja Vamshi Kiran Buyakar, Harsh Agarwal , Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma,and Antony Franklin,"Prototyping and Load Balancing the Service Based Architecture of 5G Core using NFV", in Proc. of Network Softwarization (NetSoft), 2019.
[C2] Venkatarami Reddy, Gaurav Garg, Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma,and Antony Franklin,"Interference Aware Network Function Selection Algorithm for Next Generation Networks", in Proc. of Performance Issues in Virtualized Environments and Software Defined Networking (NetSoft Workshop) , 2019.
[P1] Gaurav Garg, Venkatarami Reddy , Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma,and Antony Franklin,"DAVIS: Delay-Aware VNF Selection Algorithm for Service Function Chaining", in Proc. of Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNET), 2019. [Accepted Version]
[P2] Tulja Vamshi Kiran Buyakar, Amogh PC, Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma, Antony Franklin A, "Scalable Network Slicing Architecture for 5G", in Proc.of the 24th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking,(ACM MobiCom), 2018.[ PDF, Poster ][DOI]
[P3] Mohit Kumar Singh, Gaurav Garg, Tulja Vamshi Kiran Buyakar, Venkatarami Reddy, Antony Franklin A, and Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma "Dynamic Adaptation of Cooldown Period for Auto Scaling of VNFs", in Internet Conference, 2018.[ Poster ]
[C3] Tulja Vamshi Kiran Buyakar, Anil Kumar Rangisetti, A Antony Franklin, Bheemarjuna Reddy Tamma, "Auto scaling of data plane VNFs in 5G networks ", in Proc. of the 4th International Workshop on Management of SDN and NFV Systems co-located with International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), 2017.[ PDF ] [DOI]